NewsFeed Iranian anti-aircraft systems have shot down suspected drones near a military base in Isfahan. Iran says it was a
LATEST NEWS
LATEST NEWS
TECHNOLOGY

Wall Street doesn’t seem too keen on a potential Salesforce-Informatica pairing
When a significant rumor emerged last weekend that Salesforce was interested in buying Informatica, a legacy data management company that
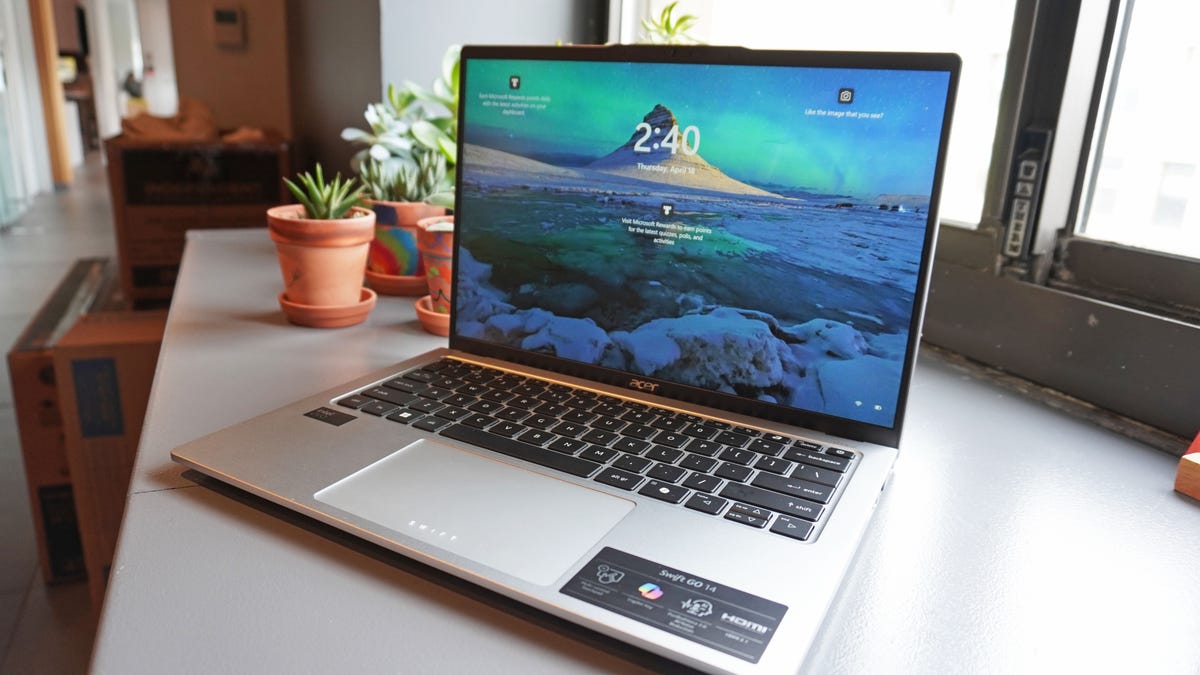

I tested Acer’s $799 AI laptop for a week and there’s one feature I can’t give up
Kyle Kucharski/ZDNET ZDNET’s key takeaways The Acer Swift Go 14 (2024) is an AI-ready ultraportable laptop that starts at $799. It’s

Webflow acquires Intellimize to add AI-powered webpage personalization
Webflow, a web design and hosting platform that’s raised over $330 million at a $4 billion valuation, is expanding into

I can’t hike without these 5 tech gadgets
I’m a big fan of Shokz bone conduction headphones, and the OpenRun Pro are without a doubt my favorite version.
Fintech CRED secures in-principle approval for payment aggregator license
CRED has received the in-principle approval for payment aggregator license in a boost to the Indian fintech startup that could
World
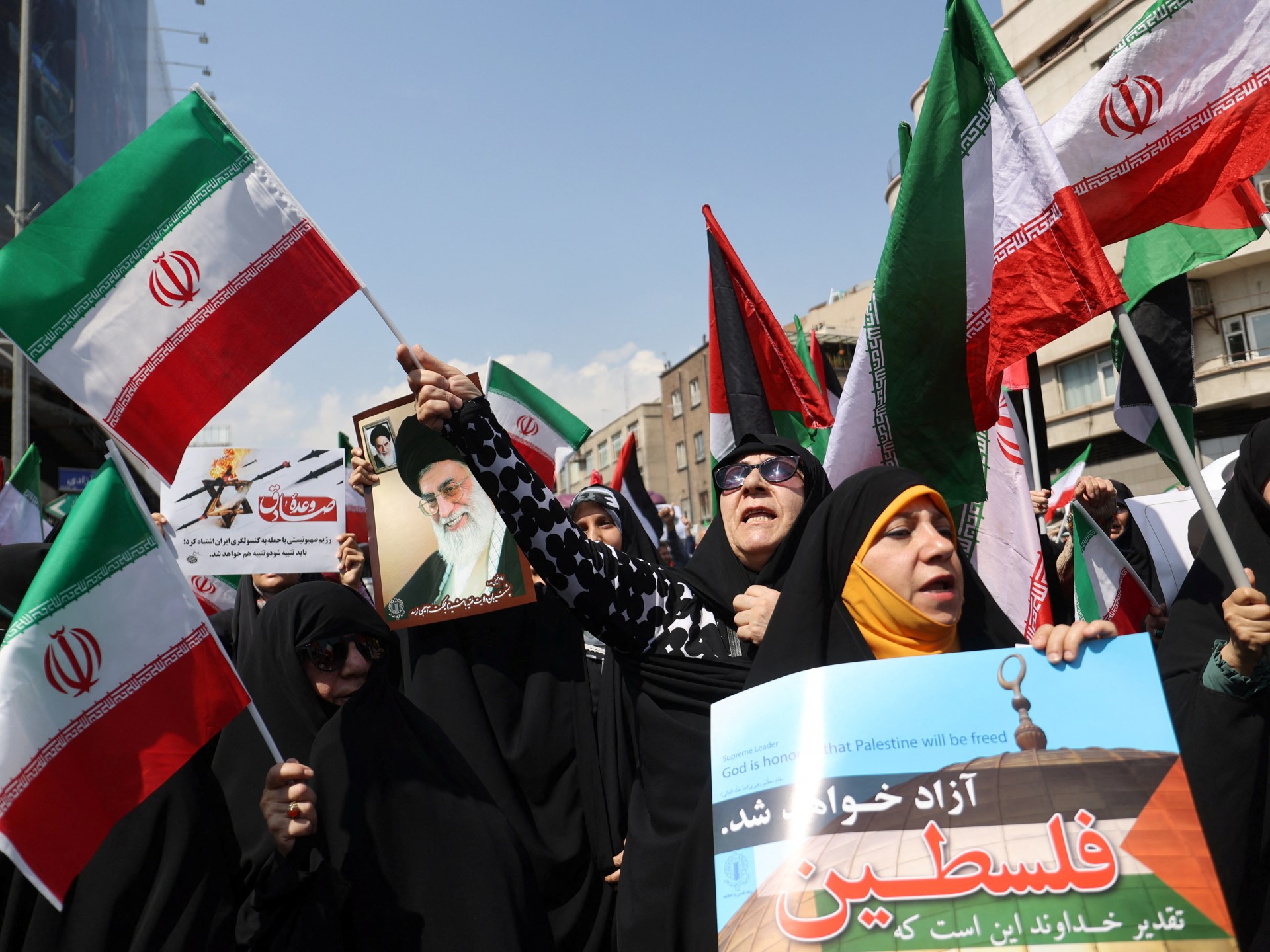

What we know so far about drone attack on Iran | Newsfeed
NewsFeed Iranian anti-aircraft systems have shot down suspected drones near a military base in Isfahan. Iran says it was a